Today, data is gold – but businesses are drowning in it. The world creates 163 trillion gigabytes of data every year (IDC), and 3 out of 4 companies say they’re lost in data chaos (Forbes). Microsoft’s answer? Two tools called Power BI and Microsoft Fabric.
Power BI (used by 30 million people monthly) helps teams create easy-to-understand charts and reports. Fabric ( 67% of the Fortune 500 are leveraging Microsoft Fabric – Hitachi Solutions) connects messy data from different sources. Though they seem different, smart companies use both, and get results:
- Make decisions 3 times faster
- Run operations 42% smoother (Forrester)
Understanding Microsoft Fabric and Power BI:
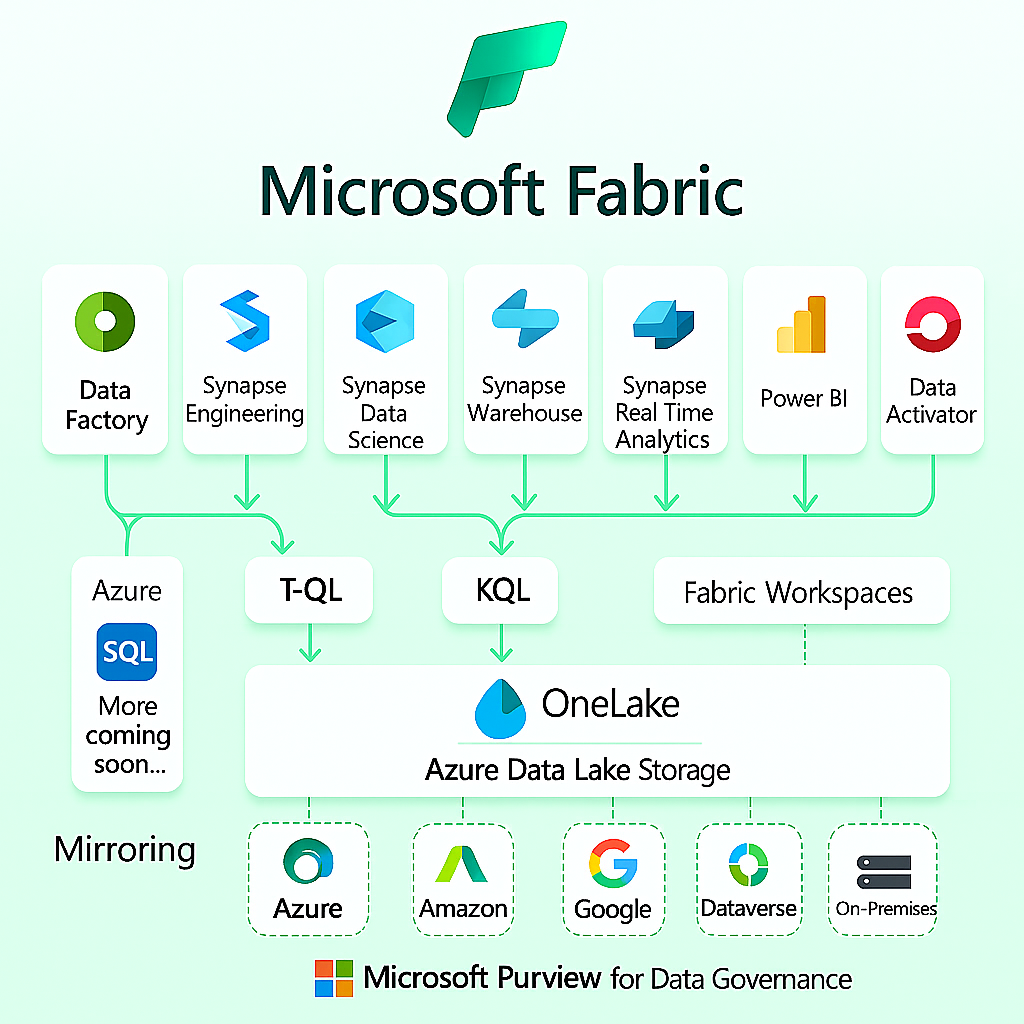
What Is Microsoft Fabric?
- Data Engineering: Tools for ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes, data pipelines, and data preparation.
- Data Warehousing: Enterprise-scale data storage with optimised query performance.
- Data Science: Machine learning capabilities and predictive analytics.
- Real-time Analytics: Processing and analysing streaming data with minimal latency
- Power BI: Visualisation and business intelligence capabilities (now integrated within the Fabric ecosystem).
- Data Governance: Centralised management of data assets, security, and compliance.
What Is Power BI ?
- Data Visualisation: Creation of interactive charts, graphs, maps, and other visual elements
- Report Building: Designing multi-page reports with various visualisations
- Dashboard Creation: Consolidating key metrics into at-a-glance monitoring interfaces
- Data Connectivity: Connecting to numerous data sources, both on-premises and cloud-based
- Data Modelling: Creating relationships between datasets and defining measures
- Sharing and Collaboration: Distributing reports and insights across organisations
Comparison Between Microsoft Fabric and Power BI:
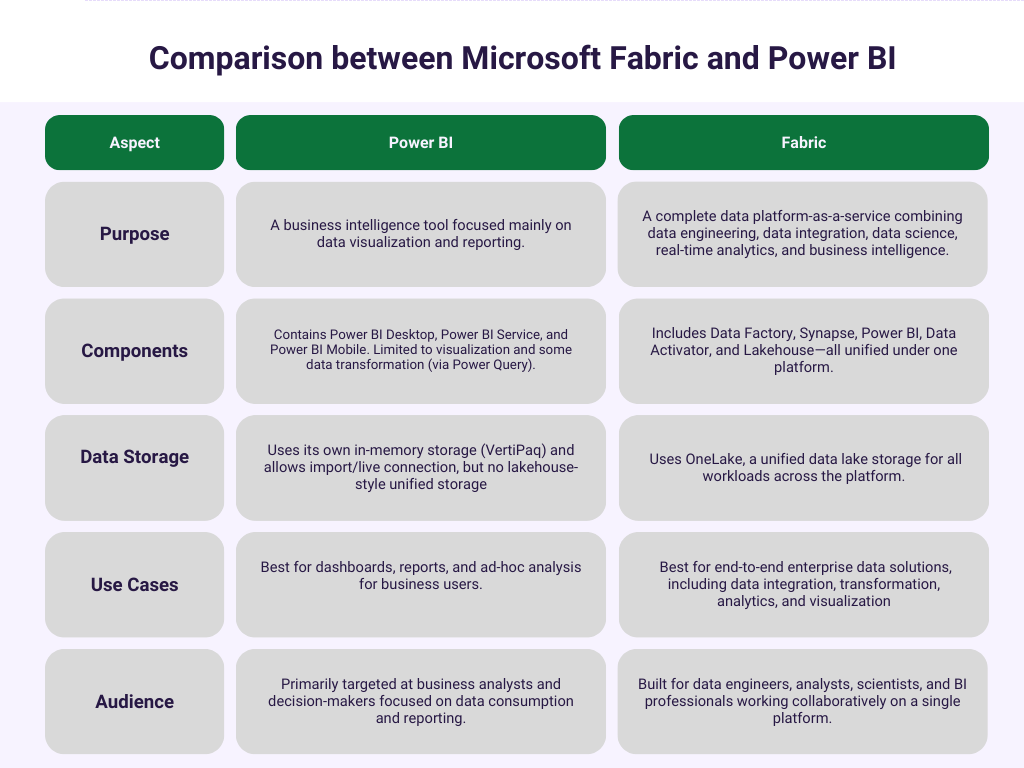
Why Your Business Probably Needs Both:
The Integration Advantage
- Data Collection and Storage: Fabric provides robust infrastructure for gathering and centralising data from various sources.
- Data Processing and Transformation: Fabric’s data engineering capabilities prepare raw data for analysis.
- Advanced Analytics: Fabric enables complex analytical models, machine learning, and statistical analysis.
- Visualisation and Distribution: Power BI transforms processed data into compelling visualisations and interactive reports.
- Actionable Insights: Decision-makers use these visualisations to drive business actions.
Different Stages of the Data Maturity Curve
- Reporting: Collecting and sharing basic business metrics
- Analysis: Exploring data to uncover trends and insights
- Prediction: Estimating future outcomes using historical patterns
- Prescription: Recommending specific actions based on insights
- Full ML lifecycle with Synapse Data Science
- Real-time data streaming via Real-Time Analytics
- Trigger-based automation using Data Activator
Cost Considerations
- Microsoft Fabric follows a capacity-based pricing model, where organisations purchase and allocate compute using Microsoft Fabric Capacity.
- It supports both Pay-as-you-go and Reserved (commitment-based) options, based on Fabric Capacity Units (FCUs).
- Power BI offers tiered licensing — Free, Pro, and Premium — each with different capabilities:
- Pro is user-based (per month per user).
- Premium offers both per-user and capacity-based licensing, ideal for larger scale deployments.
For many organisations, a balanced path looks like this:
- Use Power BI for fast, cost-effective reporting and dashboards.
- Adopt Microsoft Fabric selectively as data needs expand — e.g., data engineering, machine learning, or real-time analytics.
- Scale into full Fabric capacity when advanced use cases justify broader investment.
Technical Skills and Team Structure
For Microsoft Fabric:
- Data engineering expertise
- SQL knowledge
- Cloud infrastructure understanding
- Data modelling skills
- Machine learning capabilities (for advanced use cases)
- Data visualisation principles
- DAX formula language
- Report design skills
- Understanding of business metrics and KPIs
Making the Right Choice for Your Organisation:
Current Data Maturity
- Early Stage: Focus primarily on Power BI to establish foundational reporting capabilities
- Intermediate Stage: Implement specific Fabric components to address growing data complexity
- Advanced Stage: Deploy the full Fabric ecosystem while leveraging Power BI for widespread insight distribution
Business Priorities
- Immediate Insights: Prioritise Power BI for quick wins and visible business impact
- Long-term Data Strategy: Invest in Microsoft Fabric’s infrastructure for sustainable data capabilities
- Technical Innovation: Use Fabric’s advanced capabilities to develop cutting-edge analytical solutions.
Conclusion:
This combined approach allows organisations to address immediate business intelligence needs while building the foundation for advanced analytics, machine learning, and real-time data processing. As data continues to grow in volume, variety, and velocity, having both platforms in your technology stack provides the flexibility and scalability needed to turn data into genuine competitive advantage.
FAQ’s
No, Microsoft Fabric is not replacing Power BI. Rather, Power BI exists both as a standalone product and as an integrated component within the Fabric ecosystem. Microsoft has committed to supporting both approaches, allowing organisations to choose the implementation that best suits their needs.
Since Power BI is part of Microsoft Fabric, there’s no need to “migrate” in the traditional sense. Organisations already using Power BI can adopt Fabric components incrementally, extending their existing Power BI implementations rather than replacing them.
Small businesses typically benefit from starting with Power BI, which provides immediate value through accessible visualisation and reporting capabilities. As data needs grow more complex, specific Fabric components can be added to address advanced requirements.
Yes, Microsoft Fabric is a cloud-native solution built on Azure. Organizations requiring on-premises solutions may need to consider alternative approaches or hybrid architectures.
Yes, Microsoft Fabric includes extensive connectivity options for non-Microsoft data sources, similar to Power BI’s wide range of data connectors. This allows organisations with diverse technology stacks to consolidate their data in the Fabric ecosystem.
Implementing Microsoft Fabric typically requires knowledge of data engineering, cloud infrastructure, SQL, and data modelling. Organisations should plan for appropriate training or partnership with experienced consultants when adopting Fabric components.